Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, often resulting in a more feminine appearance. It is typically caused by hormonal imbalances, with an excess of estrogen or a deficiency of testosterone often playing a significant role. Other factors contributing to the condition include obesity, aging, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions.
Gynecomastia is a common condition affecting men and boys, characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue, often resulting in a more feminine appearance. While gynecomastia is typically harmless, it can be a source of embarrassment and discomfort for those affected, causing emotional distress and low self-esteem. The development of gynecomastia can be attributed to hormonal imbalances, with an excess of estrogen or a deficiency of testosterone often playing a significant role. Other factors contributing to the condition include obesity, aging, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Treatment options for gynecomastia depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In mild cases, treatment may not be necessary, as the condition can resolve on its own, particularly in adolescent boys experiencing hormonal fluctuations. For some individuals, addressing the underlying cause, such as discontinuing certain medications or treating a hormonal imbalance, can be sufficient in reducing the breast enlargement. When conservative treatments fail to yield satisfactory results, surgical intervention may be considered. Male breast reduction surgery, or gynecomastia surgery, involves the removal of excess breast tissue, fat, and skin, resulting in a flatter, more masculine chest contour. Gynecomastia surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and takes approximately 1-2 hours to complete. The surgical technique used depends on the specific needs of the patient, with liposuction or excision, or a combination of both, being the most common approaches. Recovery time after gynecomastia surgery generally ranges from 1-2 weeks, with most patients able to return to work and normal activities within this timeframe. It is important to follow your surgeon’s postoperative instructions closely to ensure the best possible outcome and minimize potential complications. Gynecomastia surgery can provide long-lasting results, significantly improving a patient’s self-confidence and overall quality of life.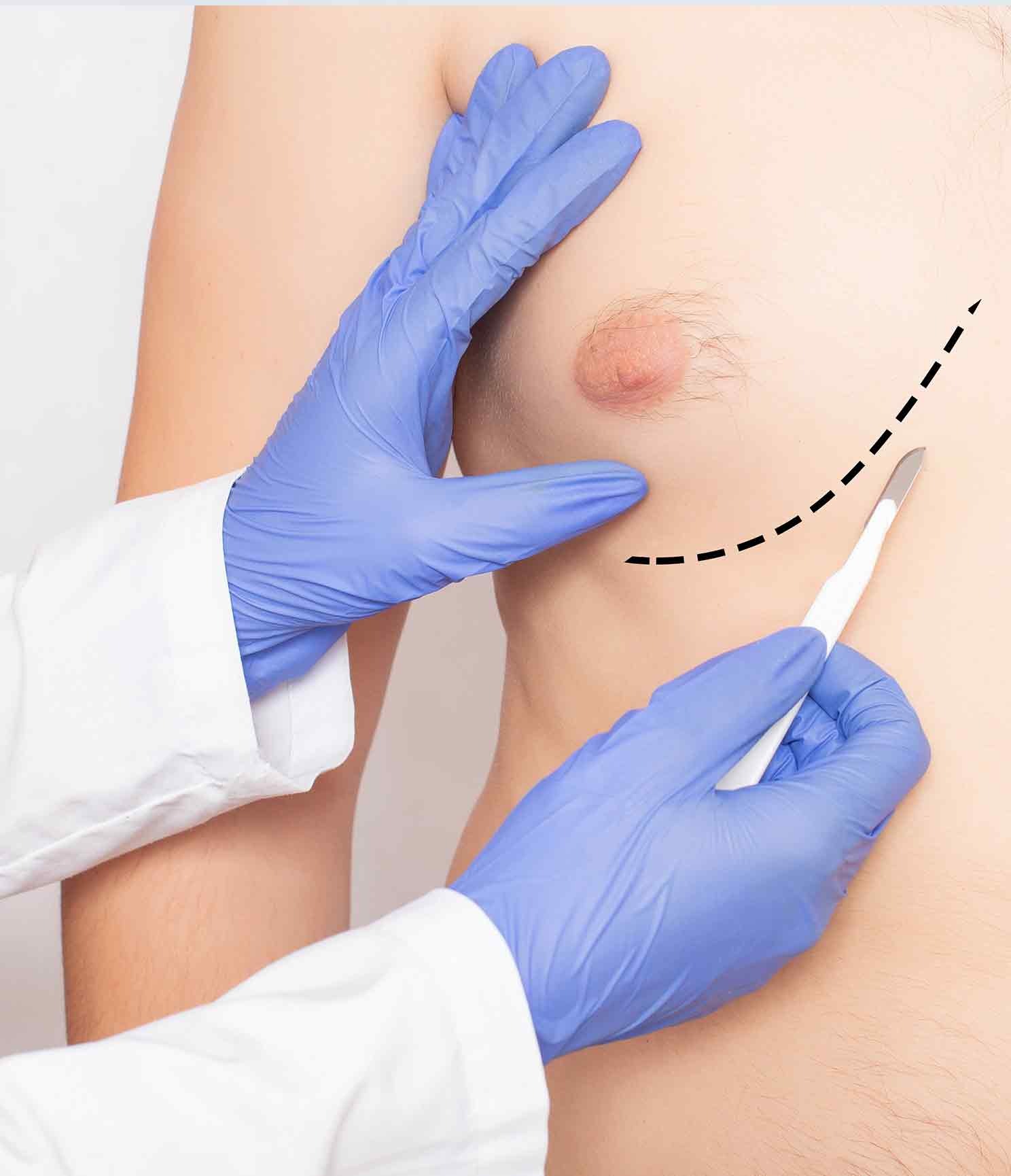
Gynecomastia
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
